Description
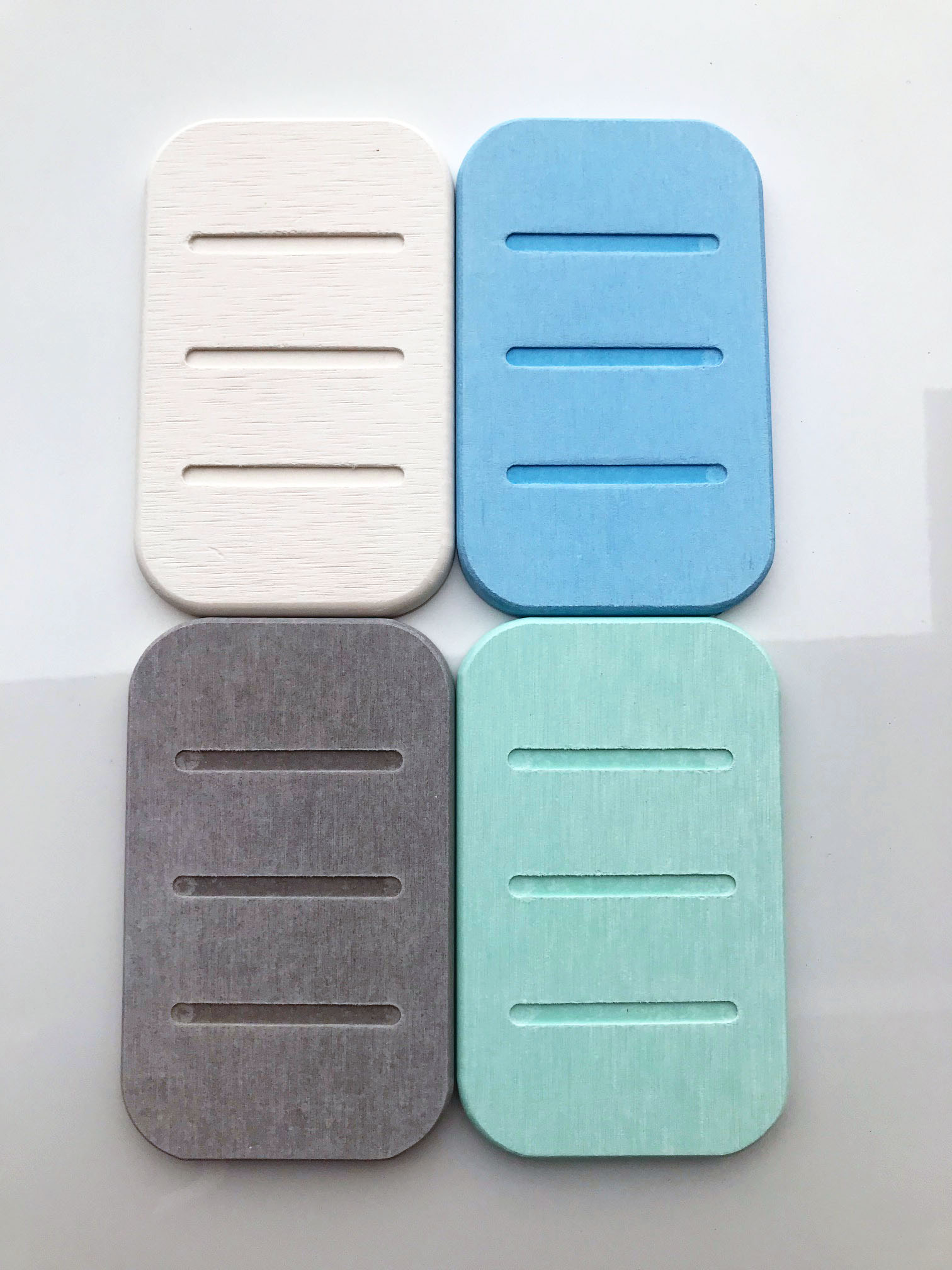
Diatomaceous Earth Soap Dish
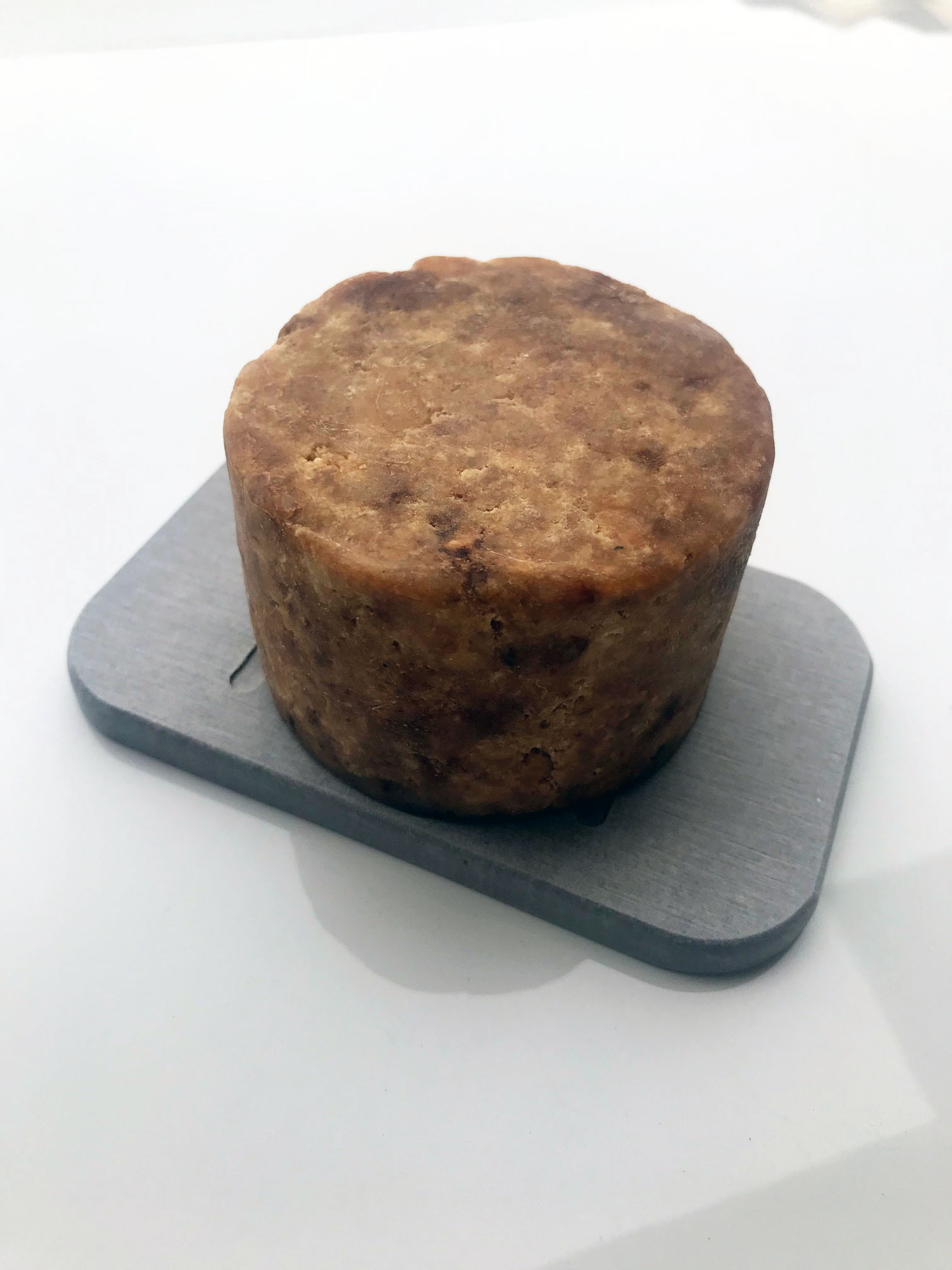
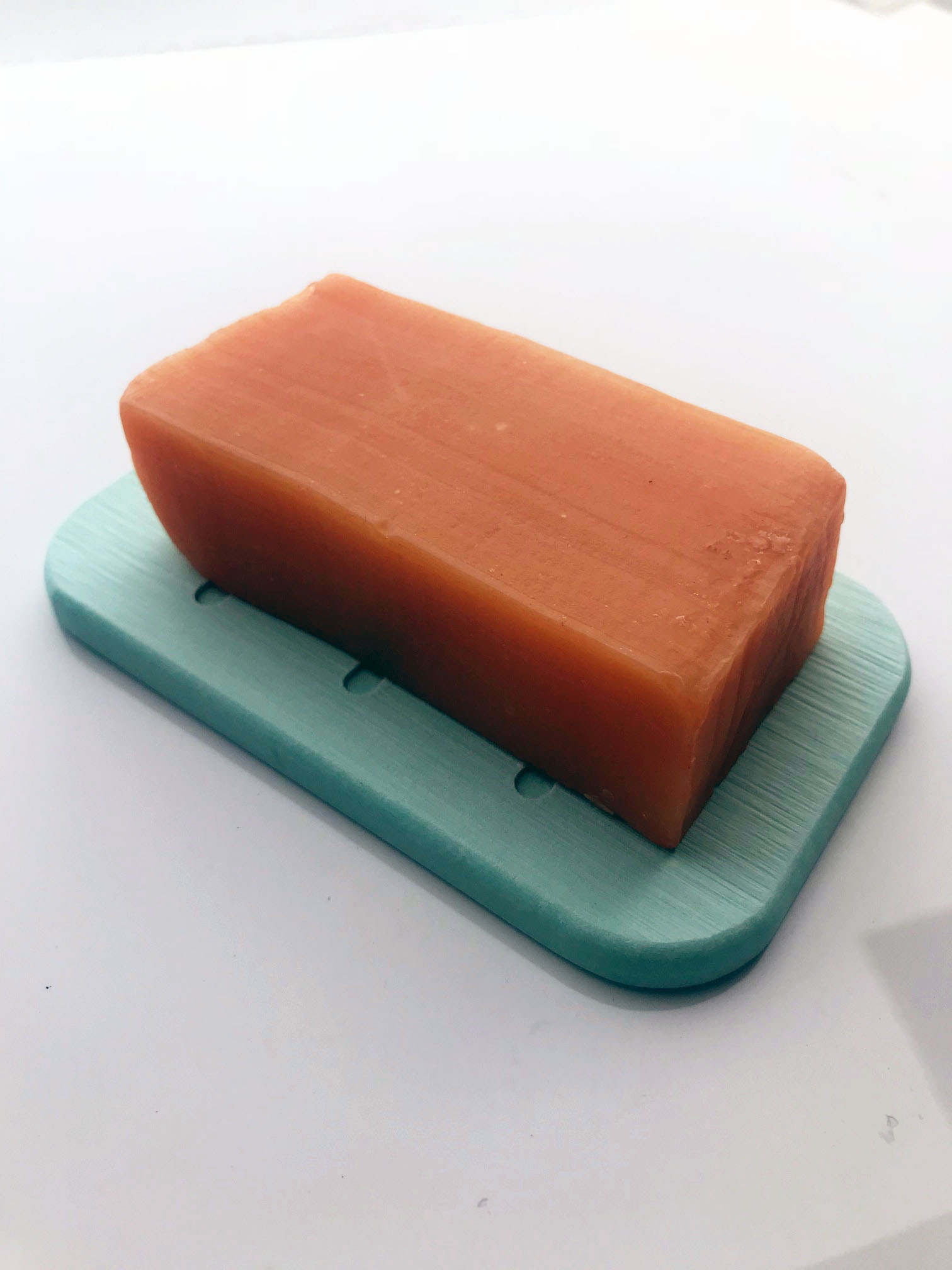
Diatomaceous Earth Soap Dish – Best soap dish to use with African Black Soap or any other type of soap. The surface dries within seconds to avoid or prevent build up of moisture and liquefied soap. Diatomaceous Earth soap dishes absorb moisture and keeps soap bars nice and clean without the mess. Diatomaceous earth soap dish dries quickly, with high water absorption and moisture-wicking properties keeps soap dish clean and dry, prevents microbial growth.
IN YOUR CHOICE OF 4 COLOURS: BLUE, GREEN, GREY, or WHITE.



See videos below for an example of how it works:
- SAFE AND CHEMICAL FREE
- MAXIMUM WATER ABSORBENCY
- ANTI-BACTERIAL
- EASY TO CLEAN
Originated from Japan. An attractive way to keep your soap or kitchen sink sponge where you want it, within reach. Strong ability in absorption. Preventing soap from getting slimy and scum, extending the life of soap.
Diatomaceous Earth
Diatomaceous earth is taken from sedimentary layers formed of phytoplankton that resided in the sea and lakes hundreds of thousands of years ago. Because it is porous with an infinite number of fine porosities on the micrometer (10-6m) scale, it has high waterand moisture retention properties, as well as deodorant and moisture control properties. A further characteristic is that it has different colors depending on the area.
From Wikpedia: Diatomaceous earth also known as D.E., diatomite, or kieselgur/kieselguhr – is a naturally occurring, soft, siliceous sedimentary rock that is easily crumbled into a fine white to off-white powder. It has a particle size ranging from less than 3 μm to more than 1 mm, but typically 10 to 200 μm. Depending on the granularity, this powder can have an abrasive feel, similar to pumice powder, and has a low density as a result of its high porosity. The typical chemical composition of oven-dried diatomaceous earth is 80–90% silica, with 2–4% alumina (attributed mostly to clay minerals) and 0.5–2% iron oxide.
Diatomaceous earth consists of fossilized remains of diatoms, a type of hard-shelled protist (chrysophytes). It is used as a filtration aid, mild abrasive in products including metal polishes and toothpaste, mechanical insecticide, absorbent for liquids, matting agent for coatings, reinforcing filler in plastics and rubber, anti-block in plastic films, porous support for chemical catalysts, cat litter, activator in blood clotting studies, a stabilizing component of dynamite, a thermal insulator, and a soil for potted plants and trees like bonsai.
Formation
Diatomite forms by the accumulation of the amorphous silica (opal, SiO2·nH2O) remains of dead diatoms (microscopic single-celled algae) in lacustrine or marine sediments. The fossil remains consist of a pair of symmetrical shells or frustules.
Discovery
In 1836 or 1837, German peasant Peter Kasten discovered diatomaceous earth (German: Kieselgur) when sinking a well on the northern slopes of the Haußelberg hill, in the Lüneburg Heath in North Germany.
TRUST ROCKET ROBIN
Rocket Robin is proud to be your supplier of truly natural products with simple ingredients in support of your family’s health and well-being.